Describe the Relationship Between Vaccination and Immunity
An understanding of the relationship between the transmission dynamics of infectious agents and herd immunity provides a template for the design of effective control programmes based on mass immunization. Since the outbreak of COVID-19 the idea of herd immunity has entered the public vernacular as a way to reduce the.
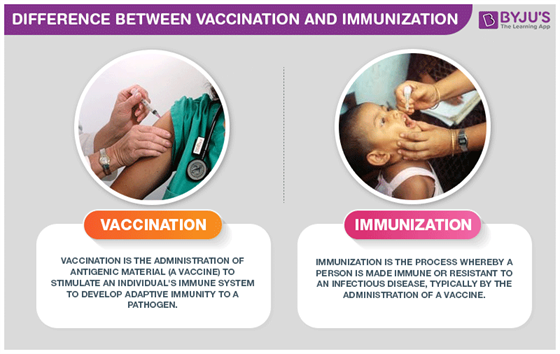
Vaccination And Immunization The Major Differences
It also suffered from survivorship bias.
. Please answer with full sentences Midnightshadow090 Midnightshadow090 6 days ago Biology College answered. However the molecular mechanisms that underlie the impairment of vaccine. The Relationship Between Vaccines and Herd Immunity.
Exposure to an infection or disease. Students will gather information and data about vaccine information. They will use this information to argue whether or not vaccinations should be mandatory culminating in a summative assessment in the form of a debate and a reflection on.
Vaccination protects more than just the vaccinated person. 8 2019 by user Ryanne Dennis user Molly Horn user Madeleine Wright Lesson Abstract. For example before the polio vaccine is administered the infant does not have immunity to the disease and has a high risk of contracting that disease.
Find an answer to your question Describe the relationship between immunity Passive and Active immunity and vaccines. Vaccines can prevent a disease from occurring in the first place and also decrease the risk of. Vaccines reduce risks of getting a disease by working with your bodys natural defenses to build protection.
Natural immunity is acquired from exposure to the disease organism through infection with the actual disease. Another persons antibodies infection-fighting immune cells When. It can come from.
Passive immunity involves the transfer of antibodies to one person produced by another person Merrill Timmreck 2006. When you receive a vaccine you are given a tiny dose of pathogens that your body is likely to defeat. However when not everyone in a population can access vaccination herd immunity becomes vital in ensuring protection.
Antibodies are proteins produced naturally by the immune system to fight disease. Acquired immunity is immunity you develop over your lifetime. Contrary to the narrative being.
In our introduction we describe the relationship between iNKTs and B cells and explore the current research hotspots and future directions. The best way to slow the emergence of COVID variants is to get vaccinated. This leads to the production of antibodies in the body.
These include children who are too young to be vaccinated people with immune system problems and those who are too ill to receive vaccines such as some cancer patients. Therefore a vaccination builds up resistance immunity to a disease. Vaccination gives us immunity without us having to experience the disease or its symptoms.
Following a vaccination a person can become immune to the specific disease. Vaccines which provide artificially acquired immunity are a much safer way to become immune. Vaccines help develop immunity by imitating an infection.
When you get a vaccine your immune system responds. Passive immunity is acquired when antibodies are introduced into the body from an external source usually through vaccines. Ad Safety is CDCs top priority and vaccination is the safest way to help build protection.
Vaccines are another common form of passive immunity. Describe the processes of isotype switching affinity maturation memory Describe the relationship between humoral immune response and vaccines Humoral Immunity Mediated by antibodies Principal defense against extracellular microbes their toxins Critical for defense against microbes with. Mathematical models of the spread and persistence of infection provide important insights into the problem of how best to protect the.
Describe the pattern when the measles vaccine was introduced between 1950 and 1968. Herd immunity or contact immunity develops in the case of certain live vaccines eg OPV wherein the nonvaccinated individuals also develop immunity to the pathogen just by coming in contact with the vaccinated individual. The term herd immunity refers to a means of protecting a whole community from disease by immunizing a critical mass of its populace.
We begin with how B cells interact and benefit from the innate and adaptive help of iNKTs. The antigens present on the surface of the pathogens act as markers that bind to the antibodies. The proportion of the population which must be immunised in order to achieve herd immunity varies for each disease but the underlying idea is simple.
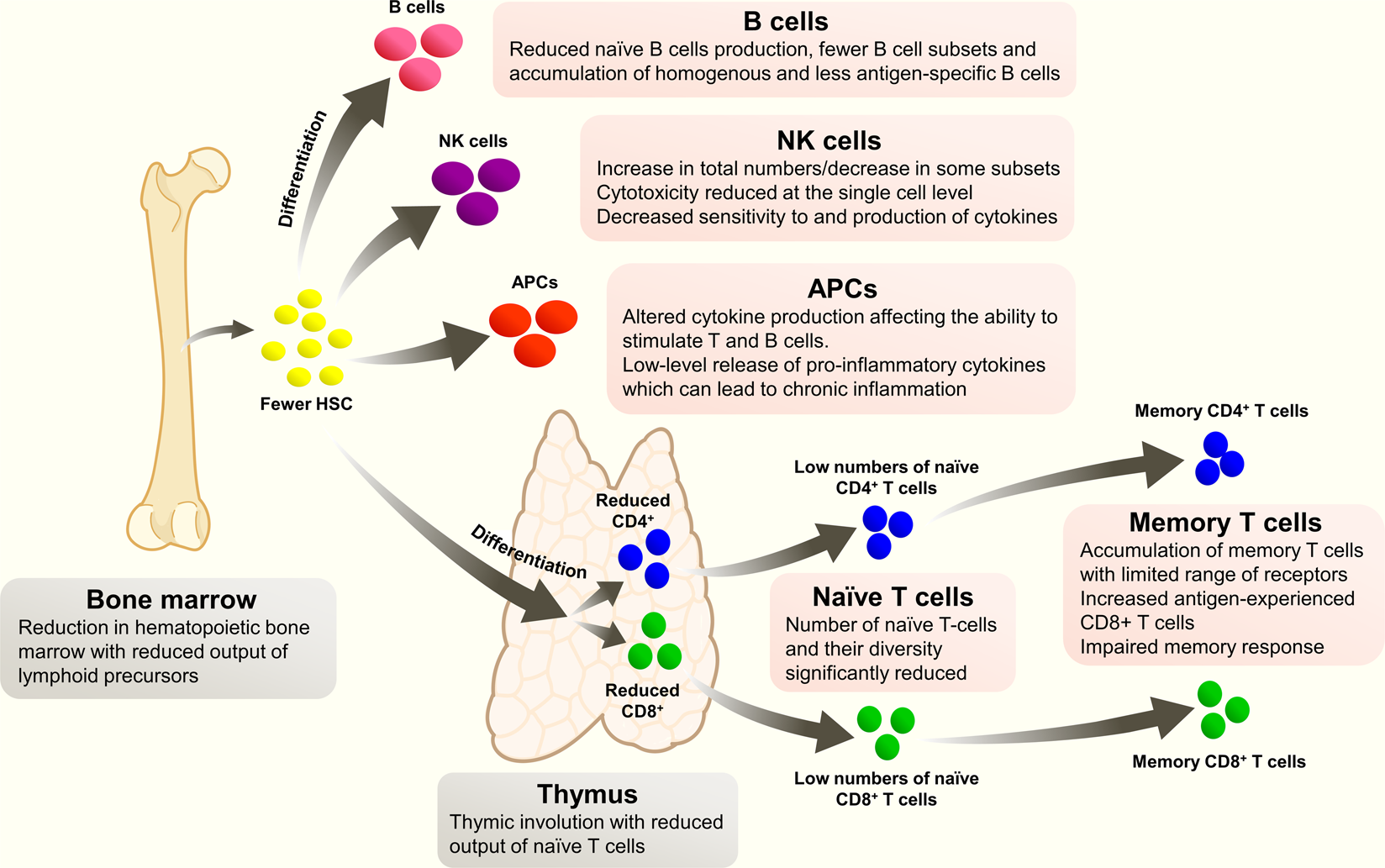
Vaccinations are crucial in the fight against infections and viral spreads. The relationship between nutritional status and immunity or between immunosenescence and vaccine efficacy is well documented 126 and it is known that the neonatal innate immune system which is biased against the production of proinflammatory cytokines impairs responses to many vaccines 127. Vaccines prepare your immune system to fight disease by taking advantage of the fact that the immune system can remember infectious organisms.
Vaccine Debate Created Aug. Sometimes after getting a vaccine the imitation infection can cause minor symptoms such as fever. Natural immunity alone is only half as effective as natural immunity plus vaccination.
Next we describe the multiple roles of these cells in infections autoimmunity and cancers. This type of infection however almost never causes illness but it does cause the immune system to produce T-lymphocytes and antibodies. Passive immunity is not considered a vaccine but can help in fighting short-lived infections.
Active immunity is attained by exposure to a pathogen. As for that Israeli study described in this presentation this study appears to have suffered from significant selection bias based on how different the populations being studied were. Active immunity can be acquired through natural immunity or vaccine-induced immunity.
Recognizes the invading germ such as the virus or bacteria. Vaccine-induced immunity is acquired through the introduction of a killed or weakened form of the disease organism through vaccination. Once enough people are protected.
Vaccines aid the immune system when warding off infectious diseases. The major difference between Vaccination and Immunization is that a vaccine is administered to people to create immunity from that disease.

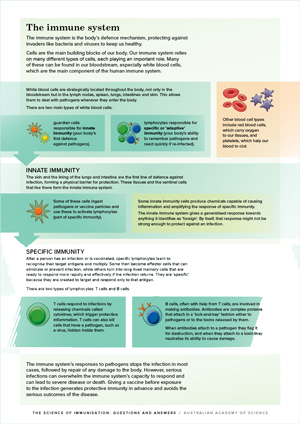
Vaccination As A Preventative Measure Contributing To Immune Fitness Npj Vaccines


Comments
Post a Comment